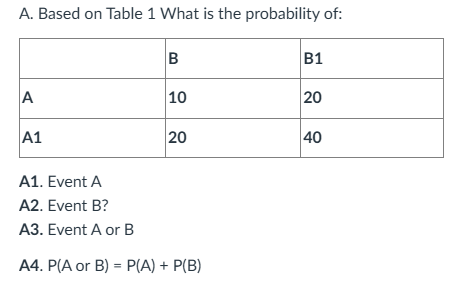
A1. Event A = row A = 10 + 20 = 30
P(A)=30/90=0.333 = 33.3%
A2. Event B = column B = 10 + 20 = 30
P(B)=30/90=0.333 = 33.3%
A3. We need P(A∪B)
- P(A)=30/90
- P(B)=30/90
- P(A∩B)=10/90
P(A∪B)=P(A)+P(B)−P(A∩B) : 30/90 + 30/90 -10/90 = 50/90 = .556 = 55.6%
A4. P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)?
- P(A∪B)=0.556
- P(A)+P(B)=0.666 Answer: False


B1. This answer is True.
B2. This result happens because rain is rare, happening only 5 out of 365 days. Even though the weatherman is 90% accurate when it does rain, the large number of nonrainy days makes most rain predictions false alarms. Therefore, the overall chance of actual rain given a rain forecast is only 11%.

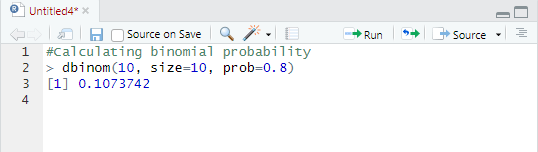
P=0.107 (10.7% chance of all 10 successes).
Leave a comment